

The DCT clutch assembly is internal and hydraulic, whereas the DDCT clutch assembly is external like a regular standard-transmission clutch. ( Figure 7).Īs with the wet DCT, the DDCT also uses a dual-clutch assembly, although they are not the same. Although controls of the DDCT are nothing like those of the DCT, internally both models function the same relating to gears, shafts, synchros etc. In addition, the valve body is mechatronic, which means that it includes the TCM.Īnother type of transmission is the “dry” DCT or DDCT (Dry Dual Clutch Transmission).

It has a slew of solenoids, sensors and valves. The 02E has a valve body to rival anything on the street ( Figure 6). None of this would be possible without proper controls, meaning a valve body. The filter is also a regular-type AT filter however, replacement requires disassembly. A normal gear-type pump provides the line pressure. The shift forks are moved hydraulically by using small molded-rubber pistons at each end of the shift fork ( Figure 5).
7 DCT TRANSMISSION DRIVER
With the dual clutch responsible for launch and gear apply, what about the shifting of the transmission? That falls to the synchronizers, just like in a manual transmission, but with one difference: The driver doesn’t do it. The frictions and steels are normal automatic-looking plates and function the same way as well ( Figure 4). The clutch plates and small-diameter piston can be replaced, whereas the large-diameter piston cannot be because of the welded assembly method chosen by BorgWarner ( Figure 3). It is a compact clutch assembly that can be partially disassembled ( Figure 2). It provides not only the initial launch of the vehicle but also all upshifts and downshifts. The dual-clutch assembly is a unique design and is used in place of a torque converter or traditional standard-transmission clutch. All the components are internal and the unit is controlled like a regular automatic.
7 DCT TRANSMISSION CODE
The DCT in Figure 1 is a “wet”-type DCT, code 02E, which was developed by BorgWarner and used by VW under the name DSG (Direct Shift Gearbox). Shifting continues in this manner up to sixth gear and back down to first. While the vehicle is being driven in first gear, the computer selects and engages second gear however, the actual apply does not happen until the large and small clutch packs reverse their apply and release status. The hollow input shaft is driven by the small-diameter clutches, which control second, fourth and sixth gears. The solid input shaft is driven by the large-diameter clutches, which control first, third and fifth gears. There are two inputs and two outputs with normal gears in between, resulting in two three-speeds rolled into one. A DCT is actually two transmissions in one, which is what allows seamless, uninterrupted shifting. What makes a DCT unique is in the design. The rest of the transmission is regular manual. The components that are colored in Figure 1 are the automatic-type items. Honda’s automatics are a departure from that scenario because of not using planetaries, although the rest of the transmission is automatic.Ī DCT certainly resembles a manual transmission more than an automatic. A basic difference between sticks and automatics has been in the gearing – planetary vs.
An automated manual is basically a traditional stick with external electrical controls (actuators).Ī DCT, on the other hand, is truly a manual transmission that has been automated ( Figure 1).
7 DCT TRANSMISSION MANUALS
“A little bit of country and a little bit of rock and roll.” Back in the late ’80s, automated manuals were developed for some high-performance applications. That is exactly what was done to create the DCT.
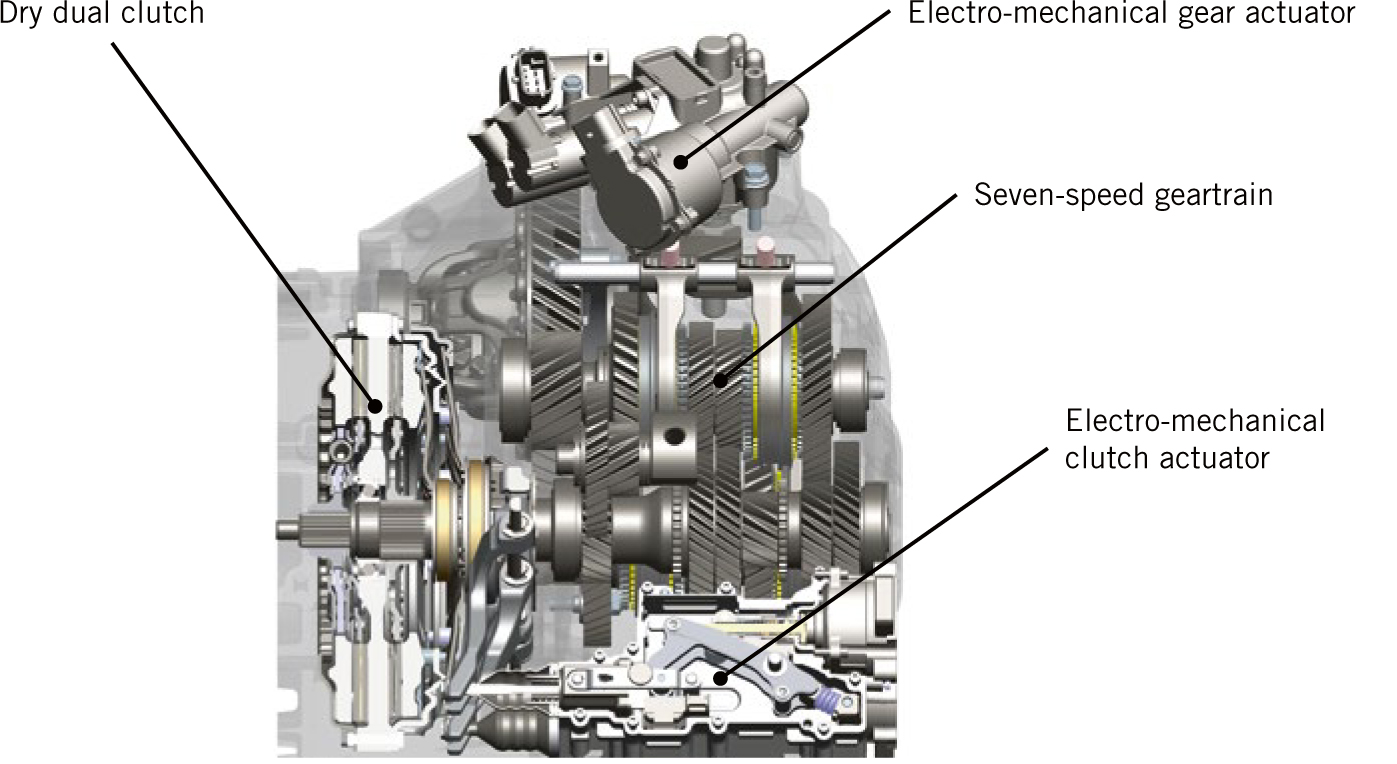
But, what about blending a manual transmission and automatic transmission together?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
